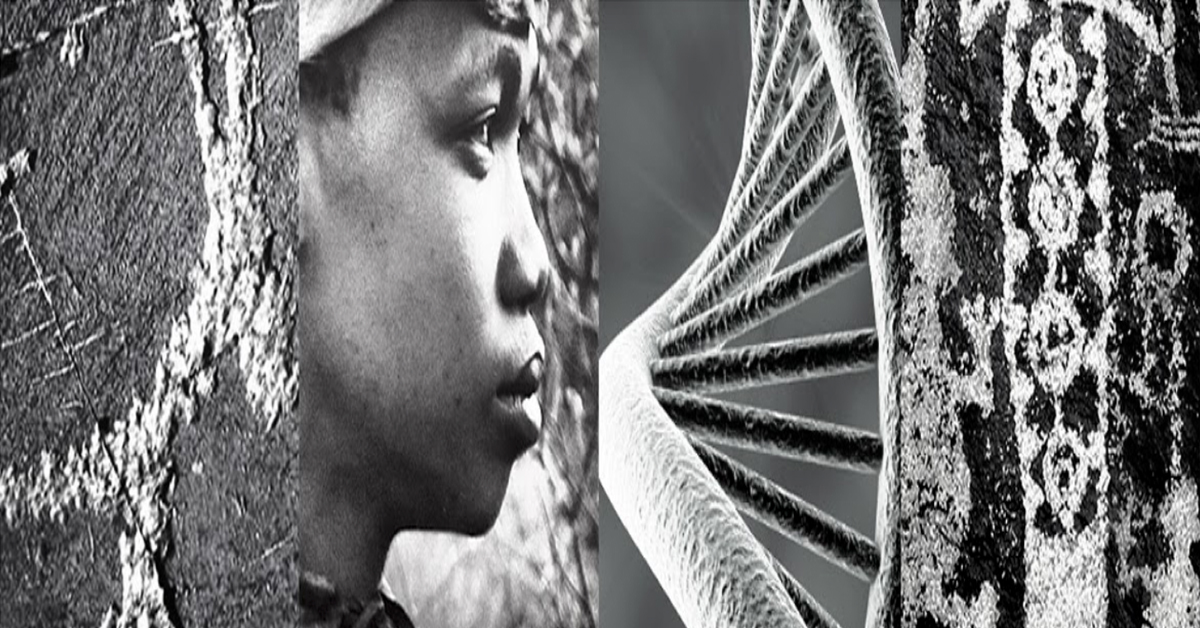
An article from the Max Planck Society on phys.org - Ancient DNA sheds light on Arctic hunter-gatherer migration to North America 5,000 years ago - reports on the new genome research on the arrival of humans in North America from Asia.
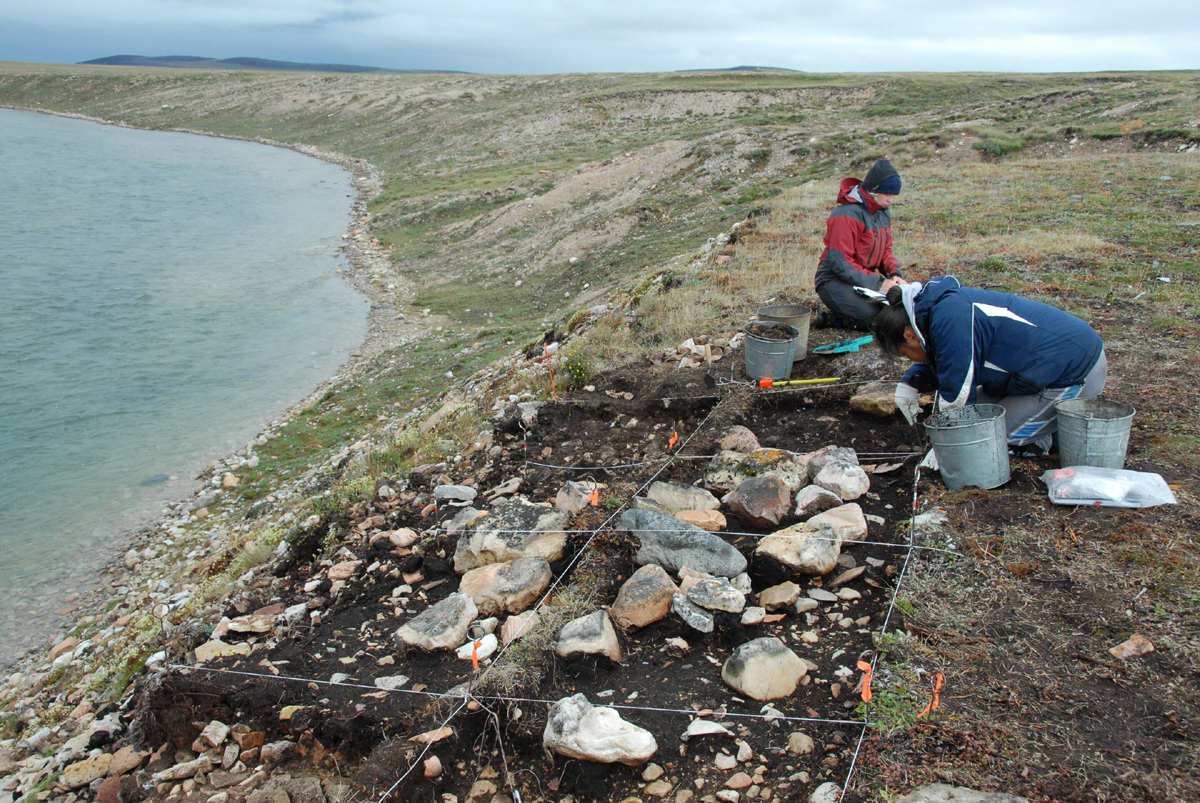

The first humans in North America arrived from Asia some time before 14,500 years ago. The next major stream of gene flow came about 5000 years ago, and is known to archaeologists as Paleo-Eskimos. About 800 years ago, the ancestors of the present-day Inuit and Yup'ik people replaced this population across the Arctic. By about 700 years ago, the archaeological evidence for the Paleo-Eskimo culture disappeared. Their genetic legacy in living populations has been contentious, with several genetic studies arguing that they made little contribution to later North Americans.
In the current study, explains Stephan Schiffels of the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, the researchers generated genome-wide data from 48 ancient individuals and 93 modern individuals from Siberia, Alaska, the Aleutian Islands and Canada, and compared this with previously published data. The researchers used novel analysis methods to create a comprehensive model of population history that included many ancient and modern groups to determine how they might be related to each other.
Paleo-Eskimos left a lasting legacy that extends across North America; a substantial proportion of the genetic heritage of all ancient and modern American Arctic and Chukotkan populations comes from Paleo-Eskimos. This includes people speaking Eskimo-Aleut languages, such as the Yup'ik, Inuit and Aleuts, and groups speaking Na-Dene languages, such as Athabaskan and Tlingit speakers, in Canada, Alaska, and the lower 48 states of the United States.
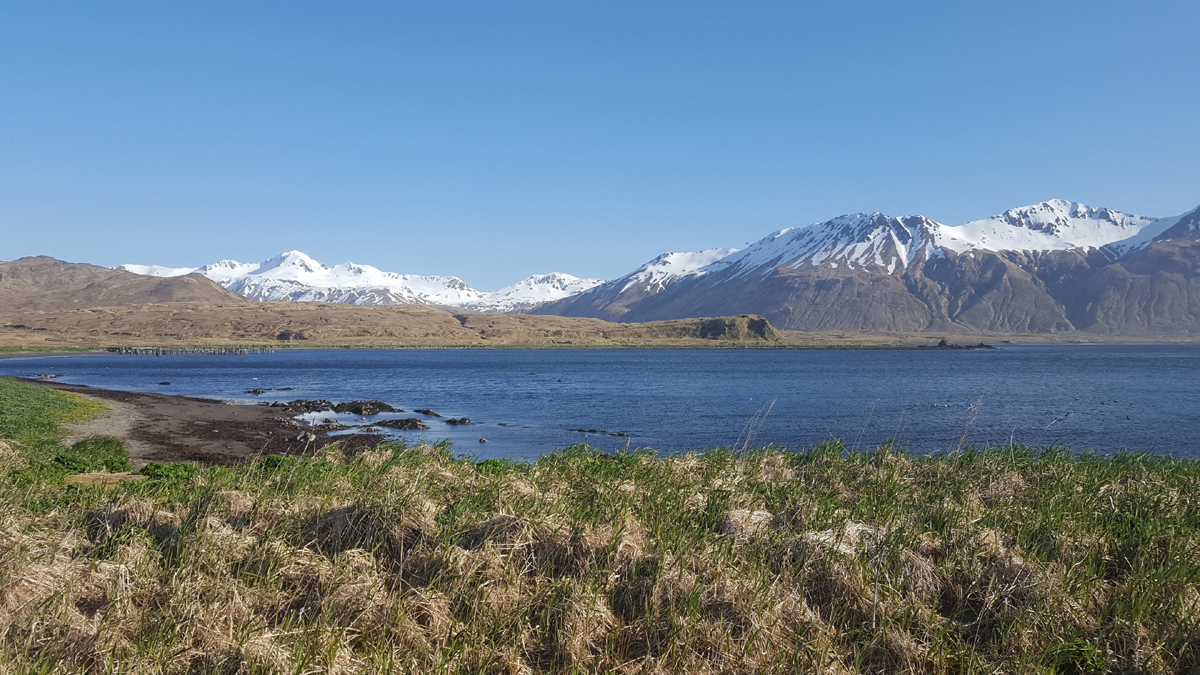

Based on the researchers' analysis, Paleo-Eskimos interbred with people with ancestry similar to more southern Native peoples shortly after their arrival to Alaska, between 5,000 and 4,000 years ago. The ancestors of Aleutian Islanders and Athabaskans derive their genetic heritage directly from the ancient mixture between these two groups. The researchers also found that the ancestors of the Inuit and Yup'ik people crossed the Bering Strait at least three times: first as Paleo-Eskimos to Alaska, second as predecessors of the Old Bering Sea archaeological culture back to Chukotka, and third to Alaska again as bearers of the Thule culture. During their stay in Chukotka that likely lasted for more than 1000 years, Yupik and Inuit ancestors also admixed with local groups related to present-day Chukchi and local peoples from Kamchatka.
Paleo-Eskimo ancestry is particularly widespread today in Na-Dene language speakers, which includes Athabaskan and Tlingit communities from Alaska and northern Canada, the West Coast of the United States, and the southwest United States.
The aim of the latest research is to provide genetic data in the context of archaeological knowledge. Pavel Flegontov of the University of Ostrava explains that determining what happened to this population was not possible from the archaeological record alone. By analyzing genetic data in concert with the archaeological data, we can meaningfully improve our understanding of the prehistory of peoples of this region.
The study is published in the journal Nature.
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 21 March 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 07 February 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 19 May 2022
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 19 October 2021
by Bradshaw Foundation
Friday 25 June 2021
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 09 November 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 03 November 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 28 October 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 23 June 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 04 June 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 14 May 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 12 May 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 19 February 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 21 January 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 20 January 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 28 November 2019
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 21 March 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 07 February 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 19 May 2022
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 19 October 2021
by Bradshaw Foundation
Friday 25 June 2021
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 09 November 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 03 November 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 28 October 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 23 June 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 04 June 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 14 May 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 12 May 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 19 February 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 21 January 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 20 January 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 28 November 2019
Friend of the Foundation