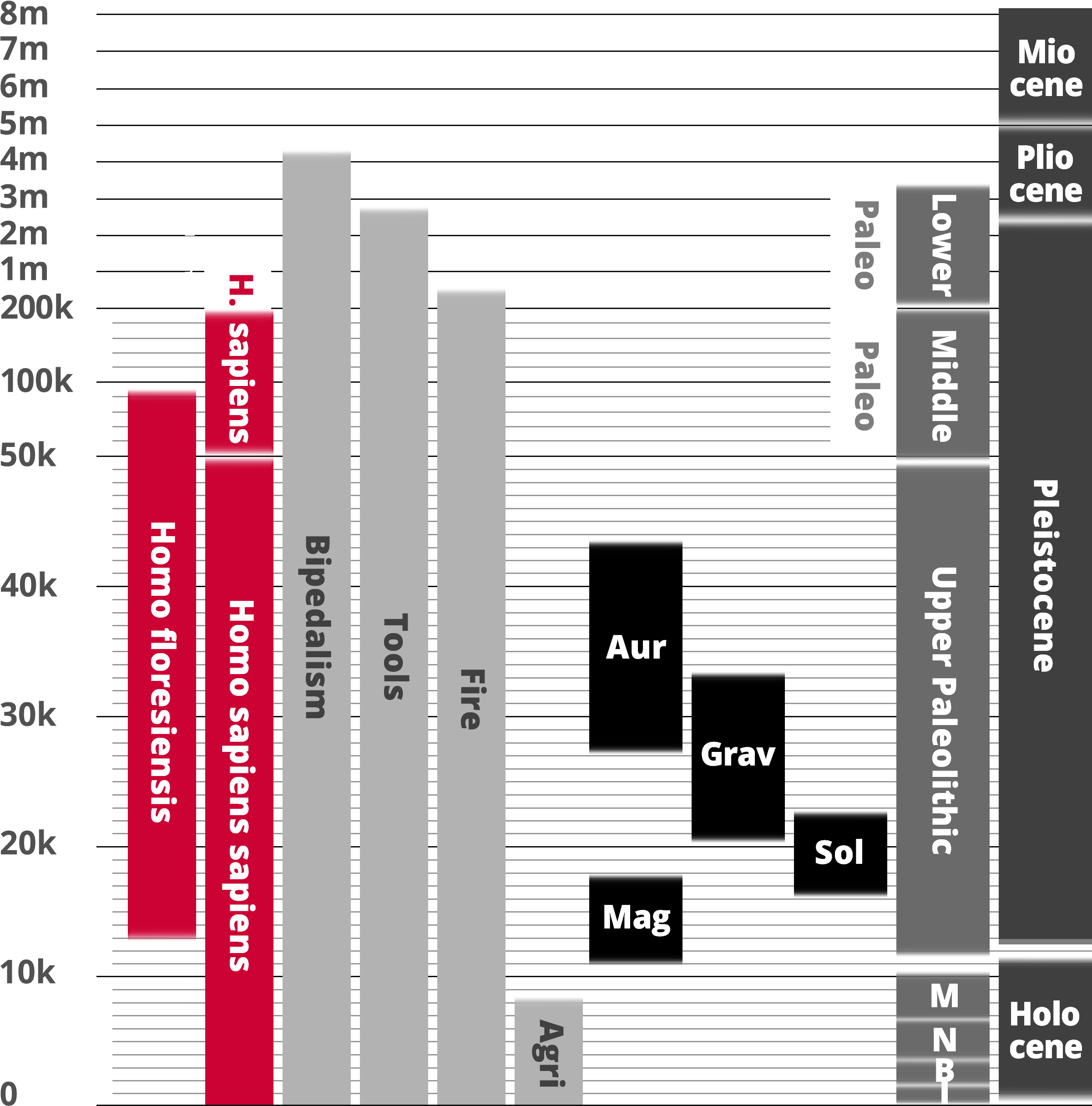
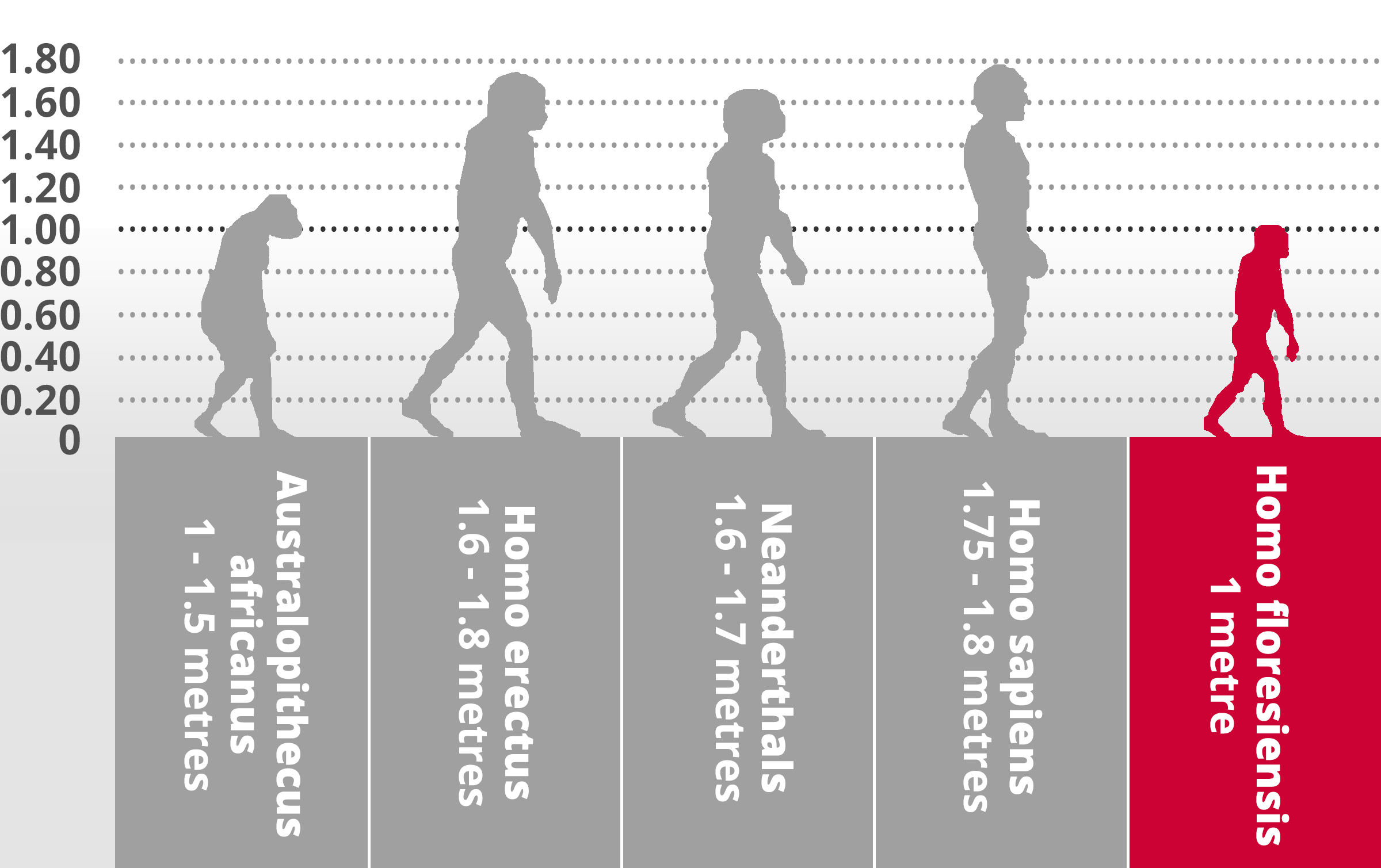
Homo floresiensis
Homo sapiens
Hominin traits
Archaeological industry/Technocomplex including art
Period in human prehistory: M = Mesolithic; N = Neolithic; B = Bronze Age; I = Iron Age;
Geological epoch
* Note: Table based past and current research and scientific consensus
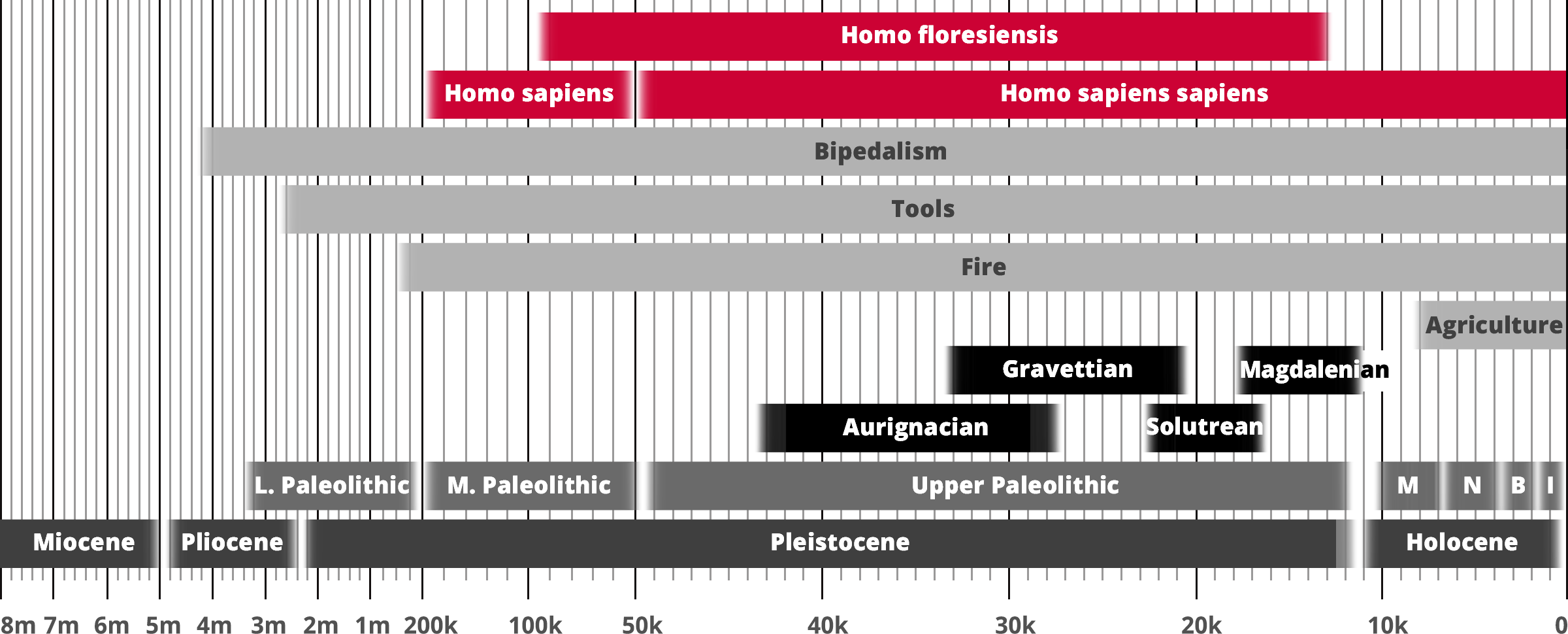
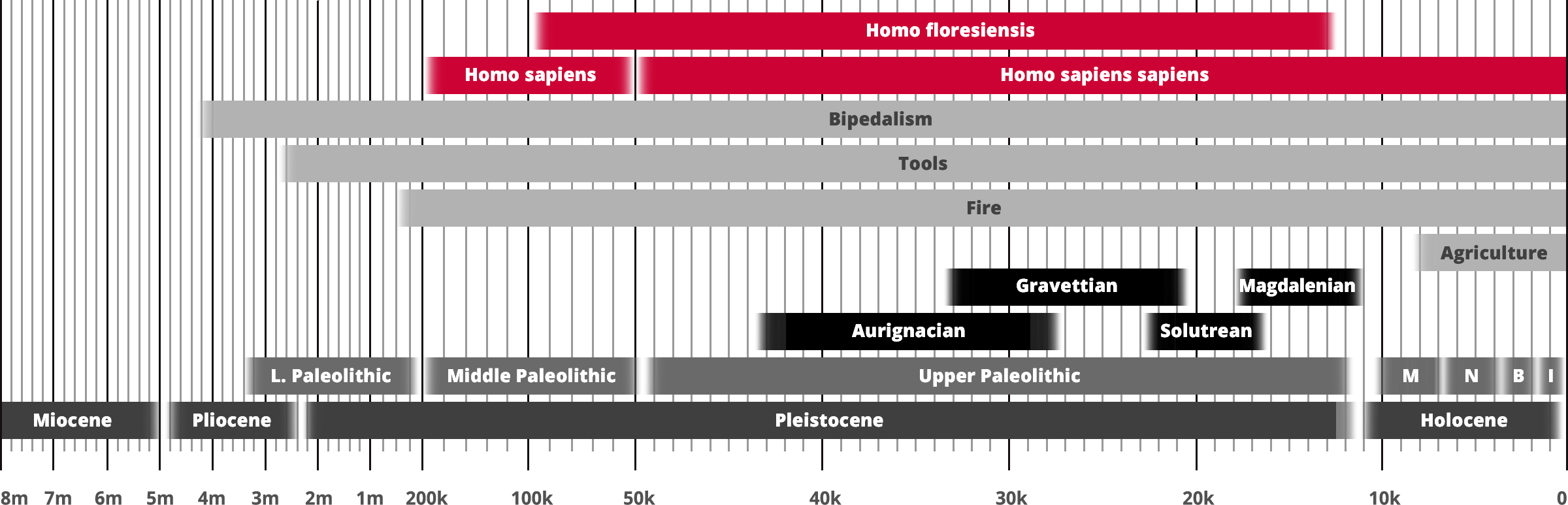
Homo floresiensis
Homo sapiens
Hominin traits
Archaeological industry/Technocomplex including art
Aur = Aurignacian; Mag = Magdalenian;
Grav = Gravettian; Sol = Solutrean
Period in human prehistory:
M = Mesolithic; N = Neolithic;
B = Bronze Age; I = Iron Age;
Geological epoch
* Note: Table based past and current research
and scientific consensus
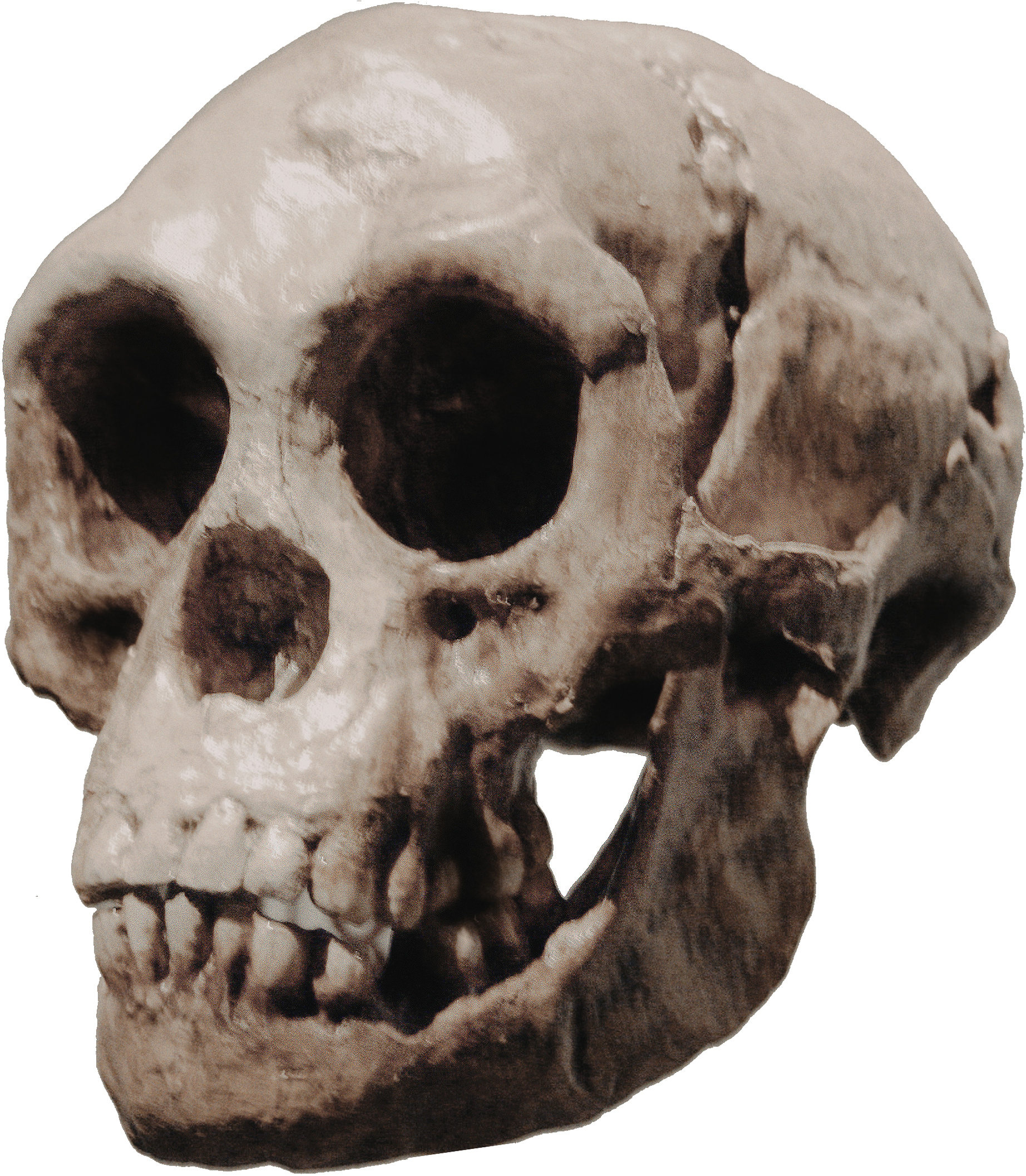
Homo floresiensis is a possible species, now almost certainly extinct, in the genus Homo. Its soubriquets include 'Flores man', 'hobbit' and 'Flo'. The dates from archaeological horizons range from 94,000 to 13,000 years ago. The archaeological remains were discovered by Mike Morwood and team in 2003 on the island of Flores in Indonesia. Partial skeletons of nine individuals have been recovered, including one complete skull, in the Liang Bua Cave.
The primary characteristic of this hominin is its small body and brain, given its survival until relatively recent times, possibly 12,000 years ago. Stone tools were recovered alongside the skeletal remains.
The overriding question is whether Homo floresiensis is a species distinct from modern humans, as Morwood suggests. He also proposes that Homo floresiensis lived contemporaneously with modern humans on Flores [Morwood, Brown et al. 2005].
Opposing Morwood’s view, some such as Teuku Jacob argue that the skull was a microcephalic [abnormally small head] modern human, although counter arguments reject this possibility [Falk et al. 2005]. Studies have gone on to reveal bone similarities with early hominins and australopithecines, but not Homo sapiens; in other words, support for the separate species hypothesis.
Subsequent excavations have recovered seven additional skeletons, dating from 74,000 to 13,000 years ago. Sophisticated stone implements of a size considered appropriate to the 1-meter-tall human are also widely present in the cave. The implements are at horizons from 95,000 to 13,000 years ago.
In 2024 an article on CNN by Katie Hunt - 'Newly discovered fossils shed light on the origins of curious ‘hobbit’ humans' - reports on recent research on the hobbit-size species of ancient human that lived on the Indonesian island of Flores until about 50,000 years ago, and how it still baffles scientists in several ways.
| HOMO FLORESIENSIS |
 |
| Genus: |
Homo |
| Species: |
Homo floresiensis |
| Other Names: |
• Flores Man
• Flores
• Flo
• Hobbit |
| Time Period: |
94,000 to 13,000 years ago |
| Characteristics: |
Small Body & Brain, Stone Tools |
| Fossil Evidence: |
Partial Skeletons, Flores, Indonesia |
First unearthed in a startling discovery nearly 21 years ago, Homo floresiensis, the scientific name for the extinct species, challenged the idea that human evolution unfolded in a neat line from primitive to complex. Experts don’t know why Homo floresiensis evolved such a tiny body yet lived relatively recently, how it crossed deep ocean to reach the island of Flores, exactly where to place this diminutive 'anomaly' on the human family tree, or why it disappeared.
An analysis of newly described Homo floresiensis fossils published in 2024 in the journal Nature Communications attempts to answer some of these questions about the tiny human. The remains examined in the new study include a fragment of a humerus - the lower half of the upper arm bone - and two teeth discovered at a site known as Mata Menge, one of only two places on the island of Flores where fossils of the species have been found.
The study authors said their findings support an existing theory that the hobbits evolved their small size a long time ago and were most likely a dwarfed version of
Homo erectus, the first ancient human to leave Africa around 1.9 million years ago, with a body size and upright gait similar to
present-day humans. The remains of
Homo erectus have been found on the Indonesian island of Java and elsewhere in Asia as well as Africa. The researchers believe
Homo erectus became isolated on the island around 1 million years ago and underwent a dramatic reduction in body size during a period of around 300,000 years. Such a scaling down in size happens to other animals on remote islands in response to limited resources, the study noted.
“Perhaps, there was no need to be large-bodied, which requires more food and takes longer to grow and breed,” said lead study author Yousuke Kaifu, a professor at the University of Tokyo, via email. “The isolated island of Flores had no mammalian predators and other hominin species, so small-body size was OK.”
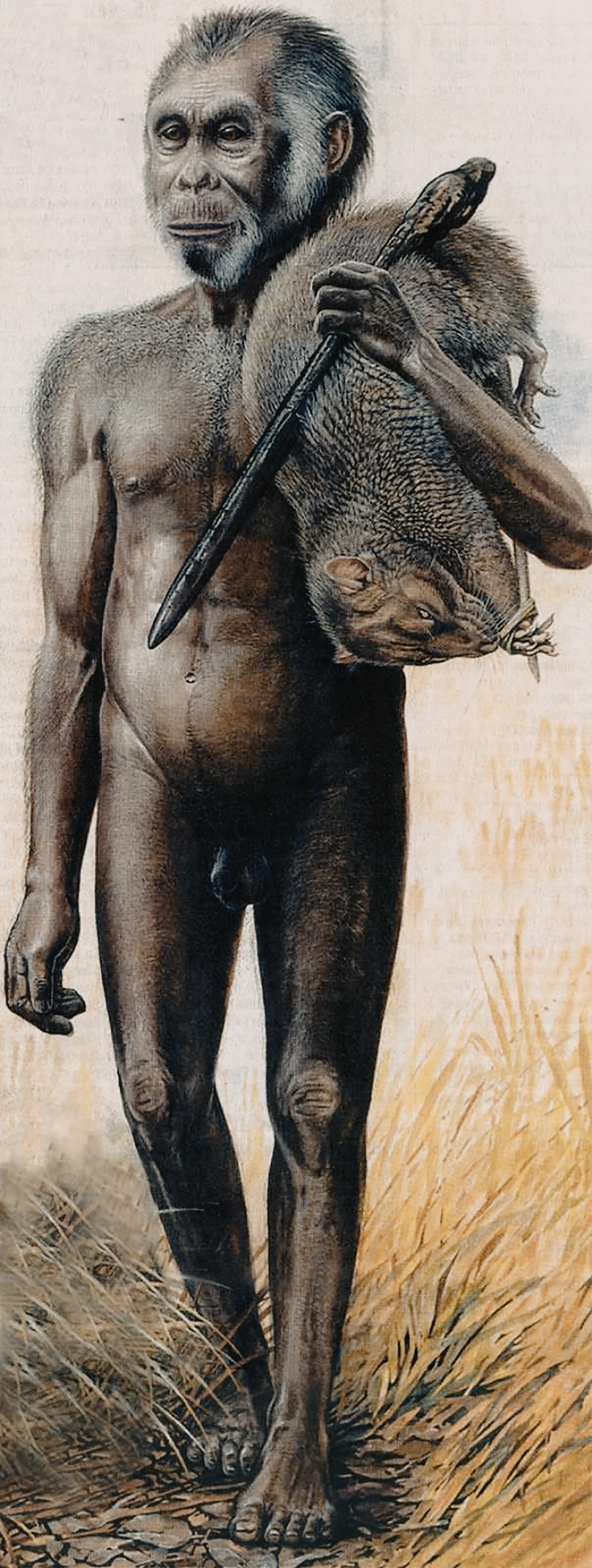

Rendering of Homo floresiensis, Flores, East Indonesia
Artwork © Peter Schouten
Based on the estimated length of the bone, the team calculated the height of its owner to be 100 centimeters (about 3.3 feet) tall. Teeth found at the same site, while smaller in size, bore a “high degree of similarity” to Homo erectus teeth unearthed in Java. Digital microscopy of the bone’s structure indicated it belonged to an adult, rather than a child. The complete humerus would have been 21.1 centimeters to 22 centimeters (8.3 inches to 8.7 inches) in length, the smallest human limb bone fossil ever found. The sediment layer containing the fossils was dated in previous research to around 700,000 years ago.
And there appear to be new Homo floresiensis revelations. This early hobbit was 6 centimeters (2.4 inches) shorter than the original Homo floresiensis specimen, an almost complete skeleton found in the Liang Bua cave — around 75 kilometers (46.6 miles) west of Mata Menge in 2003 — and dated to around 60,000 years ago. Liang Bua cave is the only other place where hobbit fossils have been found. The disparity in size between the two could point to natural variation, as seen within modern human populations, the authors noted. Overall, the research suggested that the hobbit species’ small size remained remarkably constant over a long period.
 |
|
Homo floresiensis |
Homo erectus |
Homo sapiens |
| Brain |
380 cubic cm |
900cc (archaic) to 1100cc (later) |
1200cc (archaic) to 1350cc (modern) |
| Skull |
Similar to Homo erectus, though with slightly brow ridge |
Flat, thick, large brow ridges |
Short, high, small no brow ridges |
| Skeleton |
Similar to Homo erectus, but smaller, bipedal stance |
Robust, suggesting heavy musculature |
More slender slighter build |
| Livid |
Remains date 18,000 years ago, possibly existed 800,00 years ago |
c 1.9m years ago c25,000 years ago |
c 150,000 years ago to present |
The newly analyzed finds, along with other teeth, a jawbone and skull fragment, unearthed at the same site and previously described, represent four hobbit individuals. Together with the more recent Liang Bua fossils, they suggest that the tiny humans were able to thrive on the island despite the presence of predators such as 3-meter-long (9.4-feet) Komodo dragons and crocodiles. “The early dramatic reduction and subsequent stability of body size indicated that having a smaller body size on this isolated island was of benefit to the survival of these archaic humans,” the study authors said in a statement.
The hobbit, along with the subsequent discovery of two other small-bodied and small-brained hominins who lived relatively recently -
Homo naledi in South Africa and Homo luzonensis in the Philippines - and the much larger
Denisovans, has led to a wider acceptance among paleoanthropologists that there have been many diverse species of human, including several who coexisted with our own species,
Homo sapiens. Before the discovery of Homo floresiensis, many experts in human evolution thought essentially only one species of human had evolved through time, with regional variation.
Is there overall concensus regarding the ‘hobbit’ origin story? Not all scientists agreed with the study’s interpretation that large-bodied Homo erectus was the ancestor of Homo floresiensis and that the hobbit represents a dwarfed version of Homo erectus, said coauthor Gerrit van den Bergh, a senior lecturer at the Centre for Archaeological Science at the University of Wollongong in Australia. With its tiny brain case and chimplike wristbones, the hobbit may be more closely related to small-bodied hominins such as Homo habilis, only known from Africa, others have argued.
Matt Tocheri, Canada research chair in human origins at Lakehead University in Ontario, said he wasn’t convinced that the hobbit was a scaled-down
Homo erectus. “I agree that their evidence indicates that small-bodied hominins were present on Flores at least 700,000 years ago. But why does that have to mean that their immediate ancestors that first arrived on the island were larger?” said Tocheri, who is also a research associate in the Smithsonian Institution’s Human Origins Program. “I think this question remains unanswered and will continue to be a focus of research for some time to come.”
Van den Bergh said that the hobbit remains unearthed at Mata Menge were found between 2014 and 2016. However, the humerus was broken into fragments and not immediately recognized. One of the study authors painstakingly put it back together later. “The fossils occur in hard sandstone,” van den Bergh said via email. “(W)e are forced to use metal chisels and hammers to break up the sediments, and therefore some of the fossils are recovered in many pieces.”
To resolve the debate on the hobbit’s origins, hominin remains on Flores dating further back to the period when they arrived on the island, slightly more than 1 million years ago, would be needed, both van den Bergh and Tocheri said. When the hobbit was first discovered, some experts in human evolution argued the bones were those of a modern human with a growth disorder — such as microcephaly, a condition that leads to an abnormally small head, a small body and some cognitive impairment. That assertion unleashed a fierce debate but has since largely been rejected. No sign of disease was found in the humerus, according to the study. “Every tiny fragment of Homo floresiensis or any other hominin is incredibly important,” Tocheri said. “These fossils are our window to the shared evolutionary past of our species. Without them, we have no idea what was happening in the past.”