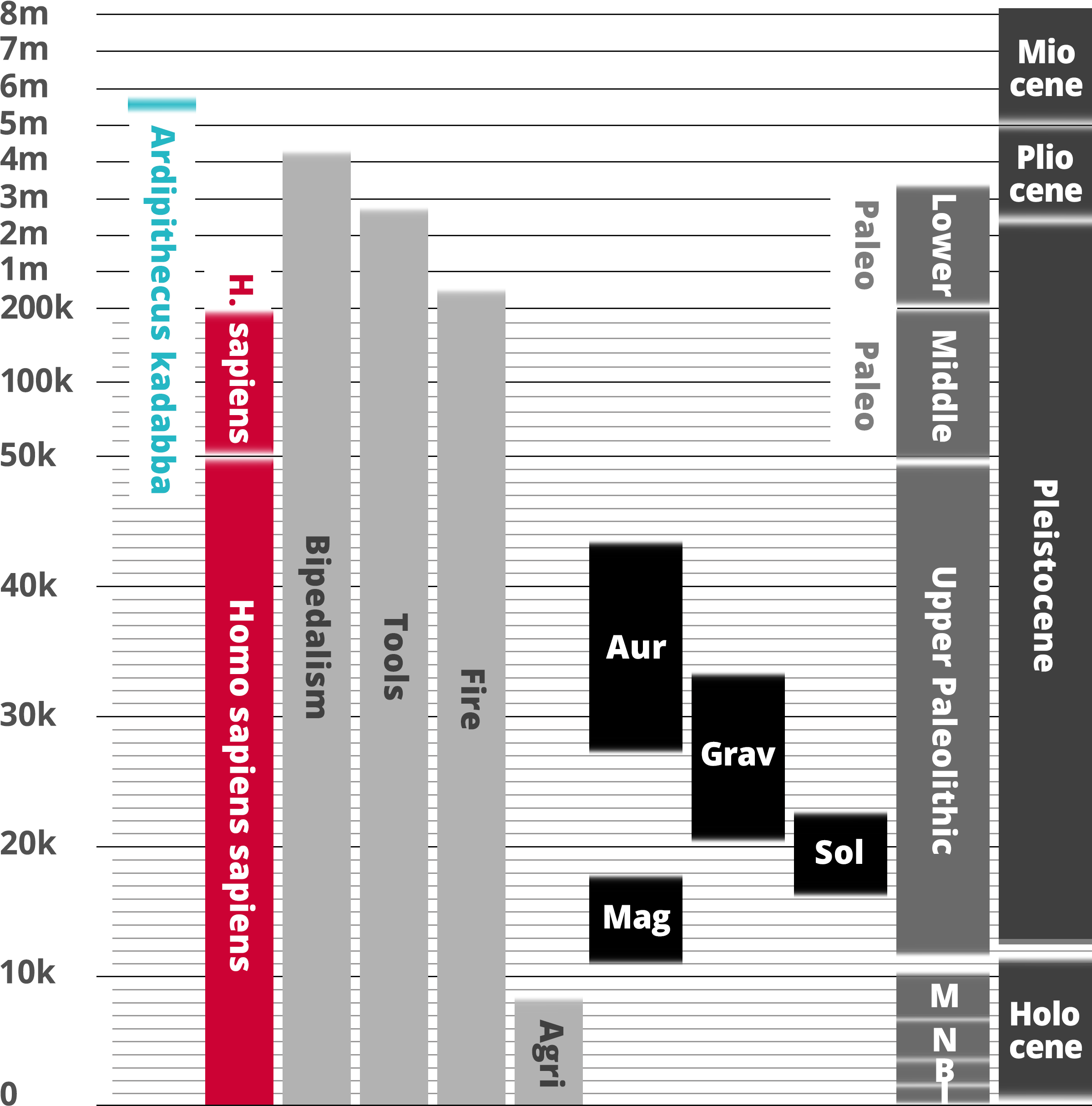
Ardipithecus kadabba
Homo sapiens
Hominin traits
Archaeological industry/Technocomplex including art
Period in human prehistory: M = Mesolithic; N = Neolithic; B = Bronze Age; I = Iron Age;
Geological epoch
* Note: Table based past and current research and scientific consensus
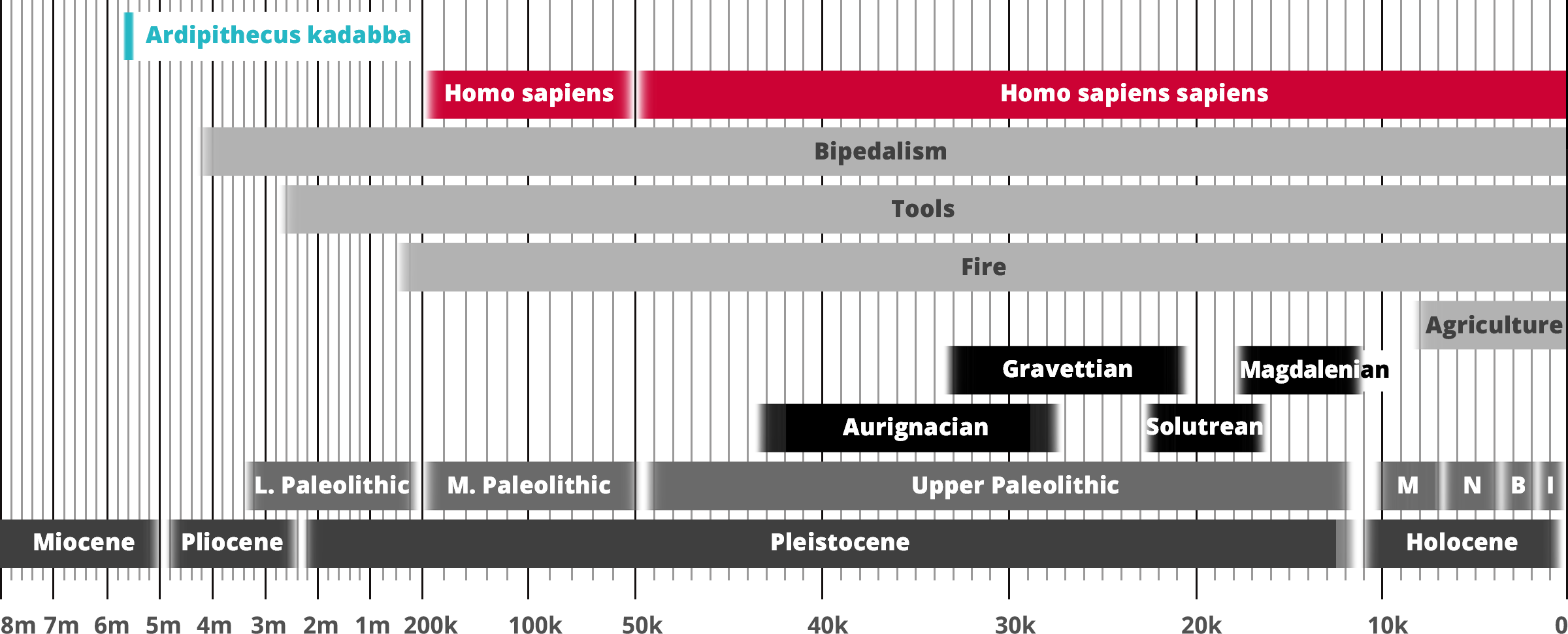
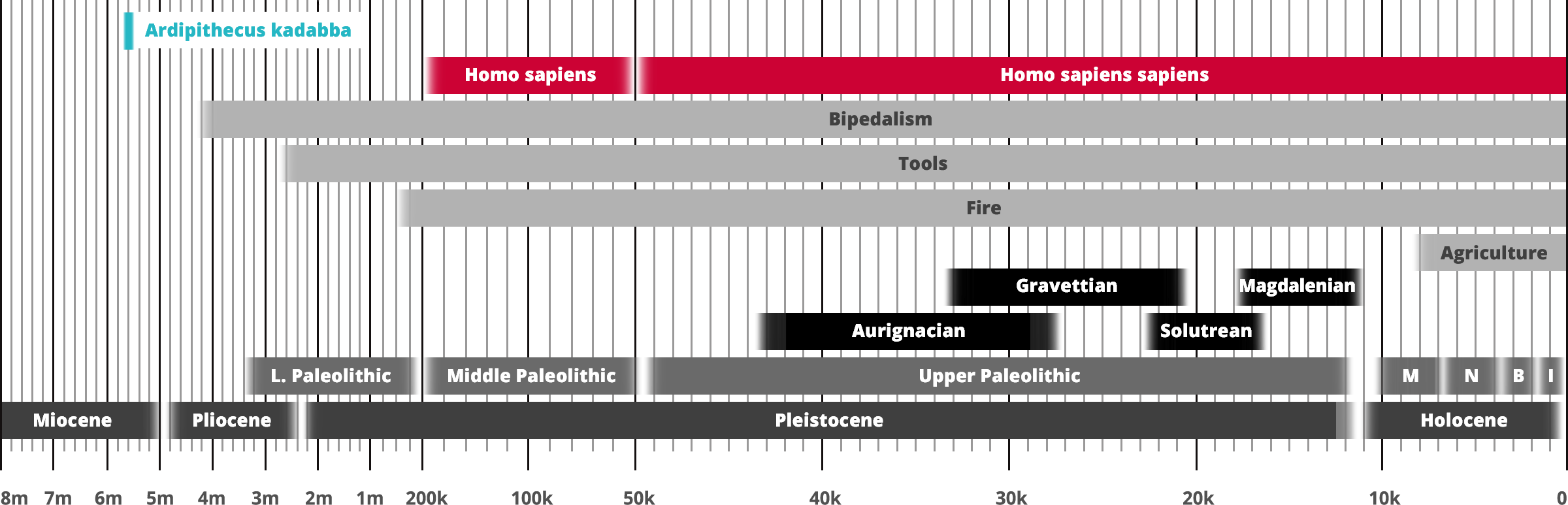
Ardipithecus kadabba
Homo sapiens
Hominin traits
Archaeological industry/Technocomplex including art
Aur = Aurignacian; Mag = Magdalenian;
Grav = Gravettian; Sol = Solutrean
Period in human prehistory:
M = Mesolithic; N = Neolithic;
B = Bronze Age; I = Iron Age;
Geological epoch
* Note: Table based past and current research
and scientific consensus
| ARDIPITHECUS KADABBA |
 |
| Genus: |
Ardipithecus |
| Species: |
Ardipithecus kadabba |
| Time Period: |
5.6 million years ago |
| Characteristics: |
Basal Ancestor |
| Fossil Evidence: |
Teeth, Skeletal Bones, Ethiopia, Africa |
Ardipithecus kadabba is a fossil hominoid, described by its discoverers as a very early hominin genus. Two species have been identified:
Ardipithecus ramidus, which lived about 4.4 million years ago during the early Pliocene, and Ardipithecus kadabba, dated to approximately 5.6 million years ago during the late Miocene [White, Tim D. et al. 2009].
Ardipithecus kadabba is known only from teeth and fragments of skeletal bones [Gibbons, Ann 2009] and is dated to approximately 5.6 million years ago. It has been described as a probable ancestor of
Ardipithecus ramidus. Although originally considered a subspecies of
Ardipithecus ramidus, in 2004 anthropologists Yohannes Haile-Selassie, Gen Suwa and Tim White [2004] published an article elevating Ardipithecus kadabba to species level on the basis of newly-discovered teeth from Ethiopia. These teeth show primitive morphology and wear pattern which demonstrate that Ardipithecus kadabba is a distinct species from
Ardipithecus ramidus.
The specific name comes from the Afar word for 'basal family ancestor'.
According to the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, Ardipithecus kadabba was bipedal, probably similar in body and brain size to a modern chimpanzee, and had canines that resemble those in later hominins but that still project beyond the tooth row. This early human species is only known in the fossil record by a few post-cranial bones and sets of teeth. One bone from the large toe has a broad, robust appearance, suggesting its use in bipedal push-off.
The discovery was made by paleoanthropologist Yohannes Haile-Selassie in the Middle Awash region of Ethiopia 1997; a piece of lower jaw lying on the ground was the first sign of a new species. Subsequently, 11 specimens from at least 5 individuals seemed to point to a new early human ancestor. The fossils - which also included hand and foot bones, partial arm bones, and a clavicle - were dated to 5.6–5.8 million years old. One of the specimens, a toe bone, is dated to 5.2 million years old; this fossil has features of bipedal walking. Faunal evidence from the site indicated that the early humans there lived in a mixture of woodlands and grasslands, and had plenty of access to water via lakes and springs.
In 2002, six teeth were discovered in the Middle Awash at the site Asa Koma. The dental wear patterns confirmed the early human fossils were unique and not a subspecies of
Ardipithecus ramidus. Based on these teeth, paleoanthropologists Yohannes Haile-Selassie, Gen Suwa, and Tim White allocated the fossils in 2004 to a new species they named Ardipithecus kadabba. There is evidence - large back teeth - that Ardipithecus kadabba ate a variety of fibrous foods as well as fruit and soft leaves.