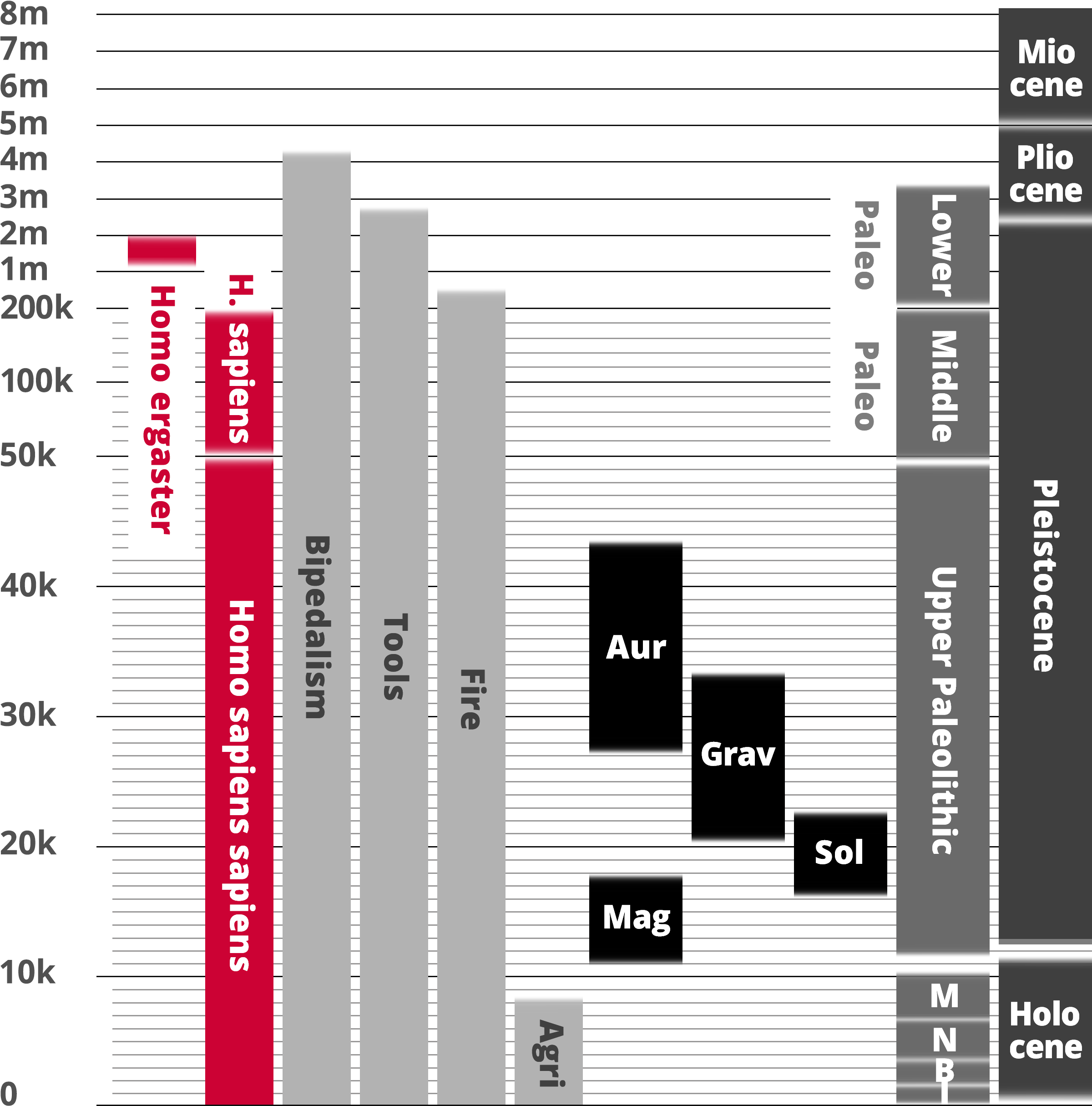
Homo ergaster
Homo sapiens
Hominin traits
Archaeological industry/Technocomplex including art
Period in human prehistory: M = Mesolithic; N = Neolithic; B = Bronze Age; I = Iron Age;
Geological epoch
* Note: Table based past and current research and scientific consensus
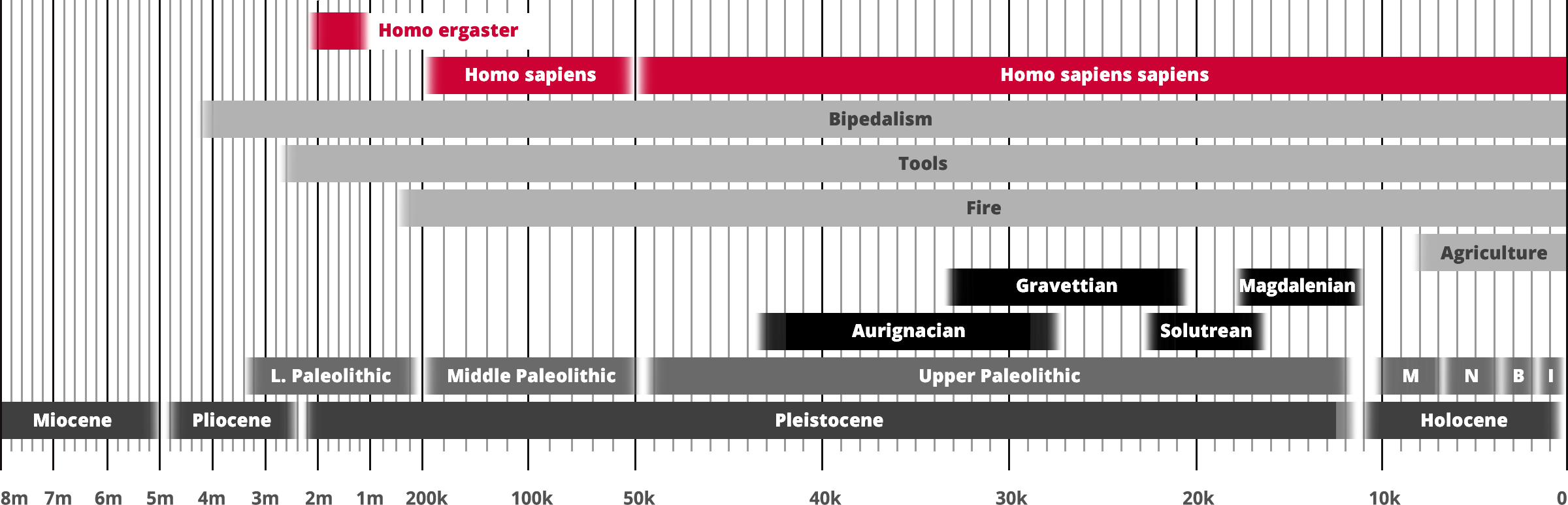
Homo ergaster
Homo sapiens
Hominin traits
Archaeological industry/Technocomplex including art
Aur = Aurignacian; Mag = Magdalenian;
Grav = Gravettian; Sol = Solutrean
Period in human prehistory:
M = Mesolithic; N = Neolithic;
B = Bronze Age; I = Iron Age;
Geological epoch
* Note: Table based past and current research
and scientific consensus
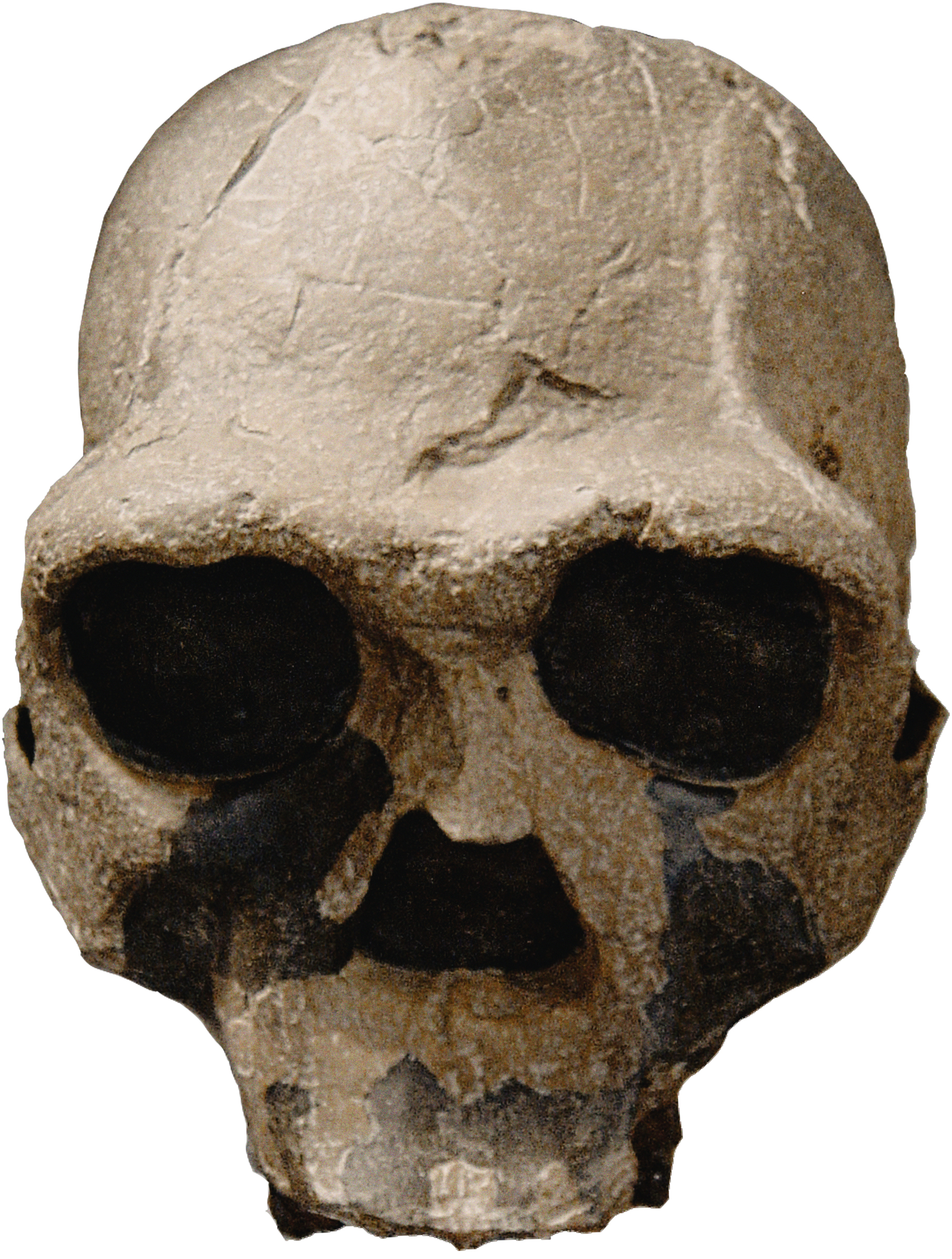
| HOMO ERGASTER |
 |
| Genus: |
Homo |
| Species: |
Homo ergaster |
| Other Names: |
• Turkana Boy
• Nariokotome Boy |
| Time Period: |
2 to 1.3 million years ago |
| Characteristics: |
Tool Maker, Proto-Language |
| Fossil Evidence: |
Complete Skeleton, Lake Turkana, Kenya, Africa |
Homo ergaster is an extinct but one of the earliest species of Homo that lived in eastern and southern Africa during the early Pleistocene between 1.8 million and 1.3 million years ago. Homo ergaster, meaning ‘workman’ due to its advanced lithic technology, is also referred to as African
Homo erectus. It was first discovered by John T. Robinson in 1949 in southern Africa. The most complete skeleton was discovered at Lake Turkana, Kenya, in 1984 by Kayoma Kimeu and Alan Walker, who nicknamed the 1.6 million-year-old specimen 'Turkana Boy'. 'Turkana Boy' and ‘Nariokotome Boy’ are sometimes classified as Homo erectus.
Homo ergaster’s use of stone tools heralded the
Acheulean industry. This term derives from the hand axes found at Saint-Acheul in France, referring to the archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture associated with early humans during the Lower Palaeolithic era across Europe, Africa, and Asia. This was the dominant technology for the vast majority of humans, with distinctive oval and pear-shaped bifacial hand axes.
Homo ergaster is believed to have diverged from the lineage of
Homo habilis between 1.9 and 1.8 million years ago, and remained stable for approximately 500,000 years in Africa before disappearing from the fossil record around 1.4 to 1.3 million years ago.
Homo ergaster displays less sexual dimorphism than its australopithecine ancestors, signifying less mating competion and greater modern social practices, resembling modern hunter-gatherer societies. It may have been the first hominin to harness fire, either as containment or as lighting. This all coincides with an increase in brain size.
Homo ergaster may well have been the first hominid to use a 'human' voice - a proto-language - based on the evidence of the cervical vertebrae. Even though there is no archaeological evidence, its well-evolved brain and physical capabilities suggest it may have made use of symbolic thought, such as figurative art.